Fraunhofer Lighthouse Project futureAM Gets Metallic 3D Printing in Shape for Industrial Use
Accelerating the additive production of metal components by at least a factor of 10: With this goal in mind, the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft launched the lighthouse project “futureAM – Next Generation Additive Manufacturing” in 2017. As the project ends in November 2020, six Fraunhofer institutes have made technological leaps forward in systems engineering, materials and process control as well as end-to-end digitalization, thus increasing the performance and cost-effectiveness of metal-based additive manufacturing along the entire process chain.
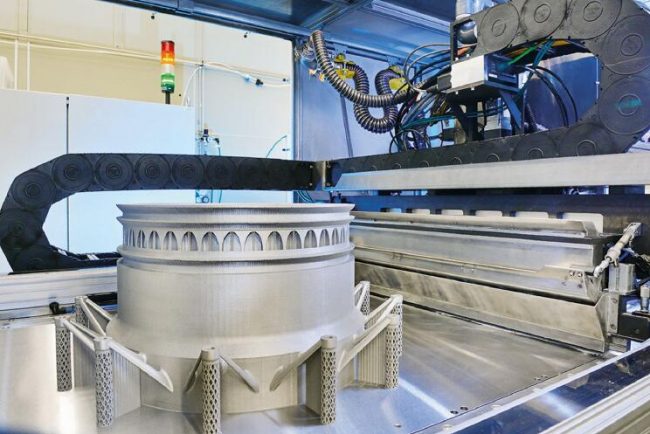 Several lasers at Fraunhofer ILT in Aachen use 3D printing to transform metal powder into a demonstrator component for the future generation of Rolls-Royce engines. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
Several lasers at Fraunhofer ILT in Aachen use 3D printing to transform metal powder into a demonstrator component for the future generation of Rolls-Royce engines. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
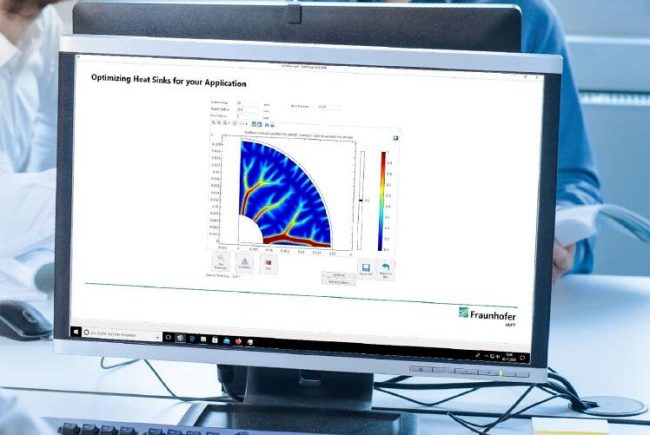 Component design using multiphysics simulations to generate production-ready 3D models at Fraunhofer IAPT, Hamburg. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
Component design using multiphysics simulations to generate production-ready 3D models at Fraunhofer IAPT, Hamburg. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
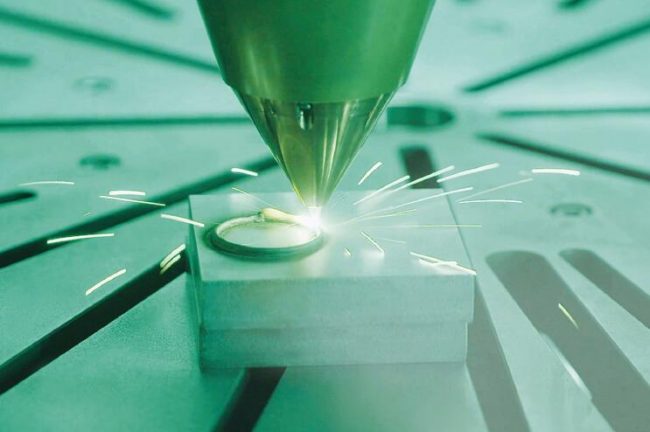 At Fraunhofer IWS in Dresden, the applicable spectrum of additive processable materials is extended. With tailored direct energy deposition metallic multi-material components can be realized. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
At Fraunhofer IWS in Dresden, the applicable spectrum of additive processable materials is extended. With tailored direct energy deposition metallic multi-material components can be realized. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
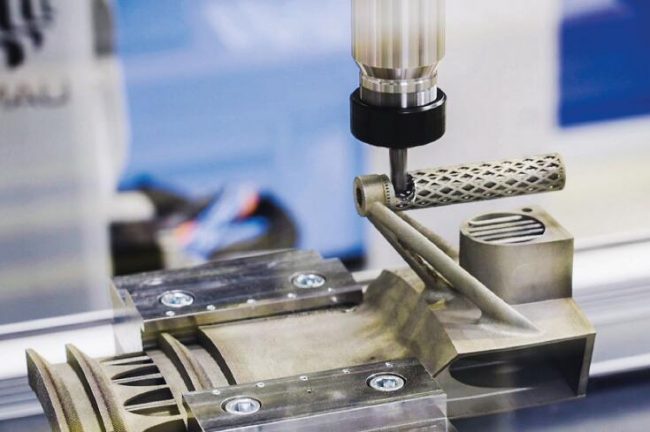 Automatic, component-specific post-processing using a robot with subsequent verification by means of 3D scanning at Fraunhofer IWU in Chemnitz. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
Automatic, component-specific post-processing using a robot with subsequent verification by means of 3D scanning at Fraunhofer IWU in Chemnitz. © Fraunhofer, Germany.
On the one hand, the futureAM partners have focused on integrating the digital and physical value chain from incoming orders to the finished metallic 3D printed component and, on the other, on making a leap forward into a new technology generation of additive manufacturing. The digital platform Virtual Lab plays an important role in this, as it pools competencies digitally and makes the entire AM process transparent for all partners involved. “We are now on the threshold of industrial implementation”, says Christian Tenbrock, group leader at the Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology ILT and futureAM project manager. “The expertise we have gained together is now to be transferred to industrial application.”
![]() Virtual Lab bundles expertise
Virtual Lab bundles expertise
A major challenge for futureAM was the interplay between all participants, some of whom cover very different areas of the entire process chain. The Virtual Lab, a digital platform that ensures the exchange of information across all AM task areas and players, has proven its worth. In this context, the Fraunhofer Institute for Additive Production Technologies IAPT has developed various software tools for the design of AM components. In this way, it has created web-based simulation tools for metal AM, tools that can also be used by beginners.
![]() Multi-material components without downstream joining
Multi-material components without downstream joining
In the “Materials” field of activity, the Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS, Dresden, has researched which materials can be combined with each other in a component and which problems arise in the process. Among other things, the Dresden researchers have dealt with expanding the applicable spectrum of additively processable high-temperature materials and researched how these can be combined in a multi-material design. The interaction of laser material deposition (LMD) and artificial intelligence (AI) yielded an exciting result: Thanks to AI-supported process analysis, the institute could analyze a wide range of influencing factors and optimize the manufacturing process. Fraunhofer IWS demonstrates how well the process already works using multi-material components made of nickel and aluminum. Depending on the component requirements, the researchers add either a third or fourth element in order to adapt the properties exactly to the respective application.
![]() Components in XXL format: Take-off 10 times faster
Components in XXL format: Take-off 10 times faster
The scientists at Fraunhofer ILT in Aachen have developed a demonstrator system built by a machine manufacturer. It is a system for 3D printing of components on an XXL scale. For example, a demonstrator component for future generations of Rolls-Royce engines could be manufactured with laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) thanks to the large build volume (1000 mm x 800 mm x 400 mm) and a new machine system with a mobile optical system. Similar successes have been achieved with extreme high speed laser material deposition (EHLA), which can now also be used to produce 3D components. The newly developed process allows extremely quick deposition speeds with high detail resolution.
![]() Automated post-processing saves resources
Automated post-processing saves resources
The researchers also identified great potential for optimization in post-processing. The Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU in Chemnitz, therefore, developed an automated solution for this as part of the project. To enable the process to identify and track the physical component beyond doubt and continuously, a code is incorporated during manufacturing and read out later. This code also ensures efficient and trouble-free copy protection. In the next step, the actual geometry of the clamped component is recorded by laser scanners and the optimum processing strategy derived by comparing the target and actual geometry. The processing is then automatically carried out by a robot and is verified in the process by renewed 3D scans.
![]() Fraunhofer Lighthouse Project “futureAM – Next Generation Additive Manufacturing”
Fraunhofer Lighthouse Project “futureAM – Next Generation Additive Manufacturing”
By founding futureAM, the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is systematically advancing the development of additive manufacturing of metallic components. The following institutes have entered into a strategic project partnership in the field of additive manufacturing:
- Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology ILT, Aachen (project coordination)
- Fraunhofer Institute for Additive Production Technologies IAPT, Hamburg
- Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Applied Materials Research IFAM, Bremen
- Fraunhofer Institute for Computer Graphics Research IGD, Darmstadt
- Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS, Dresden
- Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU, Chemnitz, Dresden
Source: Fraunhofer



Recent Comments