Additive at the Cutting Edge of Joint Replacement Surgery
German medical devices company endocon GmbH incorporates additive manufacturing to address hip cup extraction and improves product reliability, cost savings and the patient and clinician experience in the process.

![]() The Challenge
The Challenge
Hip and knee replacements are on the rise – yet another sign of our ageing population. Every year, hundreds of thousands of operations take place without a hitch and thanks to surgical and technical advances the implant of a hip cup is a relatively straightforward procedure.
However, the removal of a hip cup – in the event of loosening, abrasion or infection – presents a more complex task for surgeons with very few devices at their disposal. The removal process often involves the use of a chisel, which risks damaging bone and tissue and can leave an uneven surface, making the reinsertion a new implant difficult.
Endocon, a medical device company near Heidelberg, Germany has addressed the removal technique and has created an acetabular cut cutter. This smart, innovative device features additively manufactured blades, which reduces time in surgery and addresses both patient safety and experience.
![]() The Solution
The Solution
The endoCupcut, which was developed using GE Additive’s Concept Laser DMLM technology, allows for more precise cutting along the edge of the acetabular cup, and gives surgeons the opportunity to loosen and extract cementless hip cups quickly, without adding additional damage to the surrounding bone.
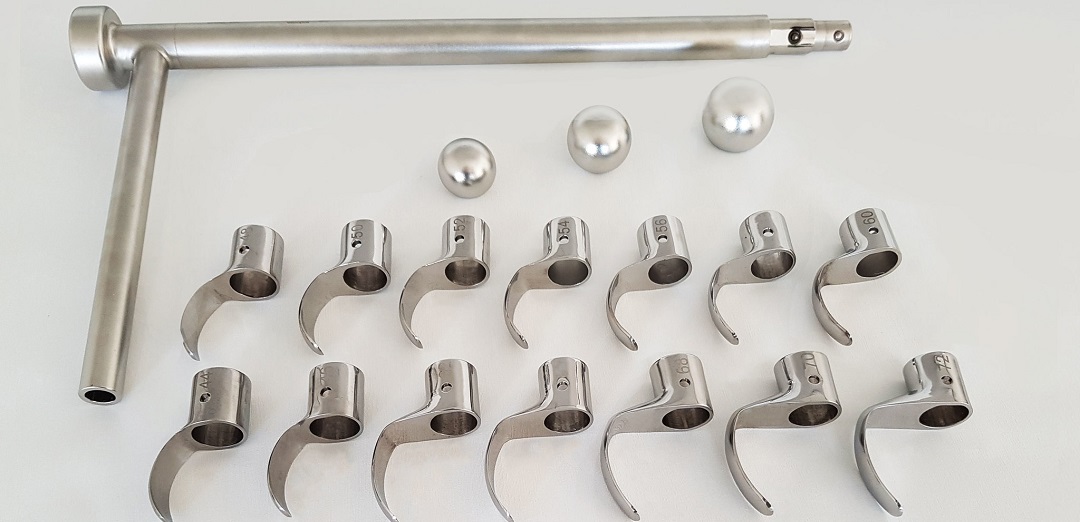

The reusable device allows surgeons to implant the same size hip cup that was implanted before. It offers variability in one instrument and can be combined with up to fifteen additively manufactured stainless steel blades, in various shapes and sizes, ranging from 44mm to 72mm.
Traditionally, cutting blades have been manufactured using traditional casting. However, relying on a time-consuming, laborious method like casting, especially for multiple sizes and shapes, meant that the production time for a single batch of blades could be as long as three and a half months.
Casted blades also often present other problems, such as corrosion, repeatable quality and difficulty achieving the consistency of the hardness, without reducing tensile strength, resulting in a rejection rate of around 30%.
![]() Additive Impact
Additive Impact
With minimal changes to the original casting model, the blades used in the endoCupcut are now additively manufactured in 17-4 PH stainless steel on a Concept Laser Mlab cusing 100R machine. The final finished blades, including post-processing, are now available in just three weeks.
“We’ve also been able to reduce the cost per blade by around forty to forty-five percent. That means cost savings for us and in turn for our customers. When you combine that with a reduction in product development time, higher efficiency and lower rejection rates, then the business case for additive really becomes attractive,” said Klaus Notarbartolo, general manager at Endocon.
A local service bureau, Weber-KP, a metal additive manufacturing specialist, manages all stages of the process for endocon. The Weber-KP team handles data preparation, orientation on the build platform, the build itself through to high-quality surface finishing, hardening and bead blasting.
Depending on size and orientation in the build envelope between two and six blades can be built on a 90x90mm build platform. Weber-KP has improved the manufacturing process to an extent, where every blade-shape has a different build orientation and support structure in the machine, to maximize the best possible outcome.
Using the Mlab cusing 100R not only provides the best quality und surface compared to other machines, it has ensured the highest possible accuracy and density, as well as significantly improving the mechanical properties of the blades.
The blades now show excellent corrosion resistance, and instead of cracking after 600 N, the additively manufactured blades show a plastic deformation after applying 1,8 kN. Previous issues with achieving a consistent hardness level of the blades have also been resolved using additive, with an improvement to 42+-2 HRC, compared to 32 HRC using casting.
The additive process has led to a more consistent outcome and the reject rate has been reduced from 30 % to under 3 %.
Harder, stronger, more reliable blades not only perform better in the operating room, they also address patient safety concerns, by reducing the risk of breakage and embedding splinters into the tissue. From the surgeons’ and the hospitals’ perspective the risk of failure is taken out of the surgery and fatigue is indicated by plastic deformation. This saves the hospital both time and money.
“Endocon’s ability to solve multiple challenges using additive is impressive example of how it can have a positive impact for smaller companies targeting the orthopedic industry. What started with the need for a reduced time-to-market in terms of product development and flexible production of various shapes and sizes has resulted in a smart, innovative medical product that enhances patient outcomes,” said Stephan Zeidler, business development manager medical at GE Additive.
“Moving the entire production process from casting to additive manufacturing was a logical step and that shift continues to provide inspiration for future projects,” Zeidler added.
![]() The Outcome
The Outcome
The device has been positively received and is already being used by a number of medical professionals across Germany. This fast and safe procedure has significantly reduced the surgery time from around half an hour to just three minutes.
Compared to the previous chisel method, the endoCupcut’s precise cutting method, preserves the maximum amount of bone substance and supports an accelerated healing process for the patient.
Manufacturing on the GE Additive Concept Laser Mlab cusing 100R machines results in exceptional part quality. Other benefits include:
- Optimal variability in one instrument, combinable with up to 15 different blades
- High-fitting accuracy of the blades through a modular system of ball-shaped heads
- Perfect fitting of the ball-shaped heads in a width of 38-60 mm
- Wear-resistant, reusable instrument for multiple operations in high-quality finishing, reliable and easy to sterilize
Source: GE Additive



Recent Comments