Novel 3D Printing Method to Fabricate Complex Metal–Plastic Composite Structures
In recent years, research interest in the 3D printing of metal patterns on plastic parts has grown exponentially, due to its high potential in the manufacturing of next-generation electronics. But fabricating such complex parts through conventional means is not easy. Now, researchers from Japan and Singapore have developed a new 3D printing process for the fabrication of 3D metal–plastic composite structures with complex shapes.

Three-dimensional (3D) metal–plastic composite structures have widespread potential applicability in smart electronics, micro/nanosensing, internet-of-things (IoT) devices, and even quantum computing. Devices constructed using these structures have a higher degree of design freedom, and can have more complex features, complex geometry, and increasingly smaller sizes. But current methods to fabricate such parts are expensive and complicated.
Recently, a group of researchers from Japan and Singapore developed a new multimaterial digital light processing 3D printing (MM-DLP3DP) process to fabricate metal–plastic composite structures with arbitrarily complex shapes. Explaining the motivation behind the study, lead authors Professor Shinjiro Umezu, Mr. Kewei Song from Waseda University and Professor Hirotaka Sato from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore state, “Robots and IoT devices are evolving at a lightning pace. Thus, the technology to manufacture them must evolve as well. Although existing technology can manufacture 3D circuits, stacking flat circuits is still an active area of research. We wanted to address this issue to create highly functional devices to promote the progress and development of human society.” The study has been published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
The MM-DLP3DP process is a multi-step process that begins with the preparation of the active precursors—chemicals which can be converted into the desired chemical after 3D printing, as the desired chemical cannot be 3D printed itself. Here, palladium ions are added to light-cured resins to prepare the active precursors. This is done to promote electroless plating (ELP), a process that describes the auto-catalytic reduction of metal ions in an aqueous solution to form a metal coating. Next, the MM-DL3DP apparatus is used to fabricate microstructures containing nested regions of the resin or the active precursor. Finally, these materials are directly plated, and 3D metal patterns are added to them using ELP.
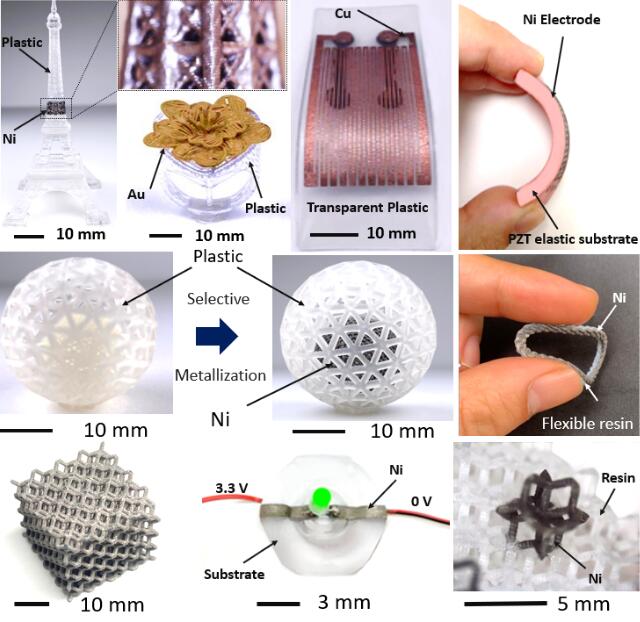 Examples of 3D metal–plastic composites that can be prepared by the new technology
Examples of 3D metal–plastic composites that can be prepared by the new technology
The research team manufactured a variety of parts with complex topologies to demonstrate the manufacturing capabilities of the proposed technique. These parts had complex structures with multimaterial nesting layers, including microporous and tiny hollow structures, the smallest of which was 40 μm in size. Moreover, the metal patterns on these parts were very specific and could be precisely controlled. The team also manufactured 3D circuit boards with complex metal topologies, like an LED stereo circuit with nickel and a double-sided 3D circuit with copper.
“Using the MM-DLP3DP process, arbitrarily complex metal–plastic 3D parts having specific metal patterns can be fabricated. Furthermore, selectively inducing metal deposition using active precursors can provide higher quality metal coatings. Together, these factors can contribute to the development of highly integrated and customizable 3D microelectronics,” Umezu, Song, and Sato state.
The new manufacturing process promises to be a breakthrough technology for the manufacturing of circuits, with applications in a diverse variety of technologies, including 3D electronics, metamaterials, flexible wearable devices, and metal hollow electrodes.
Reference
Title of original paper: New Metal−Plastic Hybrid Additive Manufacturing for Precise Fabrication of Arbitrary Metal Patterns on External and Even Internal Surfaces of 3D Plastic Structures
DOI:10.1021/acsami.2c10617
Journal: ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
Authors: Kewei Song1, Yue Cui1, Tiannan Tao1, Xiangyi Meng1, Michinari Sone2, Masahiro Yoshino2, Shinjiro Umezu1,3,*, and Hirotaka Sato4,*
Affiliations: 1Graduate School of Creative Science and Engineering, Department of Modern Mechanical Engineering, Waseda University
2Research and Development Division, Yoshino Denka Kogyo, Inc.
3Department of Modern Mechanical Engineering, Waseda University
4School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nanyang Technological University
Source: WASEDA University
For press release, welcome to send to 3D Science Valley at 2509957133@qq.com




Recent Comments